Development of method for irradiating various biological targets with focusing heavy-ion microbeam for space radiation research – Publicly Invited Research 2018-2019
- A01 Ogura
- A01 H. Takahashi
- A01 S. Takahashi
- A01 Michiue
- A01 Hinoi
- A01 Tsumoto
- A01 Nikawa
- A01 Chatani
- A01 Kawakami
- A01 Akiyama
- A01 Tomita
- A03 Suzuki
- A03 Nakamura
- A03 Harada
- A03 Kobayashi
- A03 Miyamoto
- A03 Funayama
- A03 Kakinuma
| Research Subject | Development of method for irradiating various biological targets with focusing heavy-ion microbeam for space radiation research |
|---|---|
| Research Group Leader |
 Senior Principal Researcher, Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute, Quantum Beam Science Research Directorate, National Institute for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology Website http://www.taka.qst.go.jp/rab_div/en/mrb/index_e.html |
| Research Collaborator(s) |
|
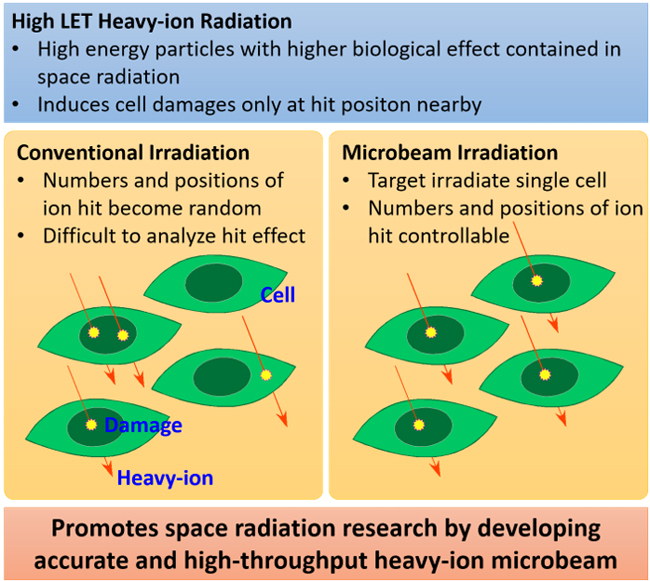
A risk of space radiation becomes more important when human stay in the space become longer by the exploration mission of the moon and Mars. Unlike environmental radiation on the ground, radiation in space contains high-LET particle radiation that is known to show higher biological effects, which are usually captured by the atmosphere and the magnetic field of the Earth. Thus, to assess risk of space radiation, analysis of radiation effect of high-LET particle radiation is necessary. However, because of dense energy deposition along with particle trajectory, dose distribution of high-LET particle on cell population become inhomogeneous and thus prevents analysis of its exact biological effectiveness when using conventional irradiation method.
Heavy-ion microbeam irradiation that target and irradiate individual cells with a micrometer sized heavy-ion beam under microscopic view is an effective means to solve this issue. In this project, we develop a method for targeting and irradiating various biological samples with a focusing heavy-ion microbeam system of QST-Takasaki.
In the research, we focus to establish a method of high-throughput irradiation of cells and small model organisms with focusing heavy-ion microbeam. To achieve this objective, we develop a specially designed cell dish for high-speed microbeam irradiation, and an irradiation software that automatically targets and irradiates individual cells of cultured cell sample and a specific region of small model organisms. By these developments, we will promote researches of space radiation effect carrying out in the “Living in Space” research project.