Genetic basis underlying the individual differences in rasiosensitivity within human populations for the future radiological protection in Space – Publicly Invited Research 2018-2019
- A01 Ogura
- A01 H. Takahashi
- A01 S. Takahashi
- A01 Michiue
- A01 Hinoi
- A01 Tsumoto
- A01 Nikawa
- A01 Chatani
- A01 Kawakami
- A01 Akiyama
- A01 Tomita
- A03 Suzuki
- A03 Nakamura
- A03 Harada
- A03 Kobayashi
- A03 Miyamoto
- A03 Funayama
- A03 Kakinuma
| Research Subject | Genetic basis underlying the individual differences in rasiosensitivity within human populations for the future radiological protection in Space |
|---|---|
| Research Group Leader |
 Associate Professor, Department of Genetics and Cell Biology, Research Institute for Radiation Biology and Medicine, Hiroshima University Website https://home.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/genome/ (*Written in Japanese) |
| Research Collaborator(s) |
|
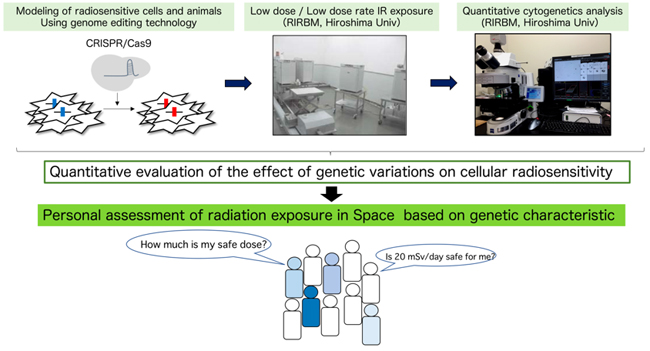
Current Japanese assessment of radiation exposure in Space is based on Publication 103 (ICRP 2007). However, the genetic heterogeneity of radiosensitivity within human populations is not considered in the current standard of radiological protection. In the future, it is expected that the personal standard of radiological protection in Space will be based on genetic factors underlying individual differences in radiosensitivity. In order to establish the safer assessment of radiation exposure in Space, here we attempt to explore the genetic variations underlying the individual differences in radiosensitivity using a combined approach of quantitative cytogenetics and genome editing technology in human cultured cells and experimental mice with a uniformed genetic background