Mechanism of microgravity sensing in muscle mitochondria – Publicly Invited Research 2018-2019
- A01 Ogura
- A01 H. Takahashi
- A01 S. Takahashi
- A01 Michiue
- A01 Hinoi
- A01 Tsumoto
- A01 Nikawa
- A01 Chatani
- A01 Kawakami
- A01 Akiyama
- A01 Tomita
| Research Subject | Mechanism of microgravity sensing in muscle mitochondria |
|---|---|
| Research Group Leader |
 Professor, Department of Nutritional Physiology, Institute of Medical Nutrition, Tokushima University Graduate School Website https://tokudai-seitaieiyo.jimdo.com/ (*Written in Japanese) |
| Research Collaborator(s) |
|
[Aim]
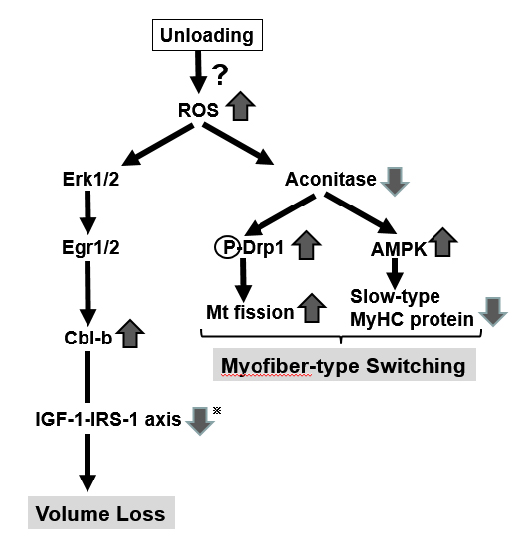
The zero gravity stress converts the energy production system of skeletal muscle from aerobic glycolysis to anaerobic glycolysis (metabolism reprogramming) (= gravity is not loaded, it requires less energy for exercise). We discovered previous grade studies that weightless stress inactivates aconitase, the rate limiting enzyme of the TCA cycle via oxidative stress, and induces metabolic reprogramming. In this study, the origin of this oxidative stress is the molecular device XXX (unpublished), and elucidate the whole picture of the microgravity sensing mechanism (microgravity sensor).
[Results]
- "Induction of oxidative stress in myocytes by weightlessness and simulated weightlessness": In Myolab space experiment, L6 cells were launched into space and metabolome analysis was performed, suggesting accumulation of oxidative stress. Therefore, when measuring oxidative stress using 3D-Clinorotation which is one of simulated microgravity models on the ground, It was found that the oxidative stress production increased at an early stage as 0.5 hours after 3D-Clinorotation was started. Furthermore, it was identified that its oxidative stress is super oxide anion.
- "Expression of ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b by oxidative stress": We found two pathways via oxidative stress involved in waste muscle atrophy. The first one is a pathway of increased expression of Cbl-b via the transcriptional regulatory factor Egr 1/2, which reduces muscle mass. To investigate the upstream factor of Cbl-b, we analyzed the promoter region of the human Cbl-b gene by oxidative stress using the luciferase assay and it was found that upstream -111 bp to -60 bp showed oxidative stress responsive An increase in luciferase activity was observed. The supershift assay using the upstream sequence candidate protein showed that the expression of Cbl-b is oxidative stress inducible Egr 1/2.
[Plan]
We have already found that decomposition of YYY (unpublished) that maintains the XXX structure is enhanced when the mouse is subjected to tail suspension (simulated microgravity). Therefore, we analyze the correlation between XXX collapse and mitochondrial dysfunction by electron microscopy or molecular biological techniques.