Elucidation of muscle atrophy mechanism from space environment – Publicly Invited Research 2018-2019
- A01 Ogura
- A01 H. Takahashi
- A01 S. Takahashi
- A01 Michiue
- A01 Hinoi
- A01 Tsumoto
- A01 Nikawa
- A01 Chatani
- A01 Kawakami
- A01 Akiyama
- A01 Tomita
| Research Subject | Elucidation of muscle atrophy mechanism from space environment |
|---|---|
| Research Group Leader |

|
| Research Collaborator(s) |
|
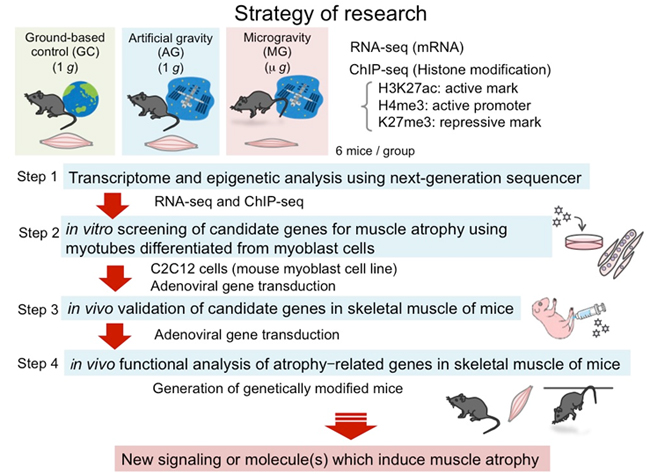
Disuse muscle atrophy is muscle atrophy caused by not using muscles such as bedrest and the function of skeletal muscle is seriously impaired. Since Japan is entering an aging society in recent years, disuse muscle atrophy is one of the major social problems to be solved. But effective prophylactic and therapeutic methods have not yet been established. On the other hand, the speed and degree of muscle atrophy caused in the space is approximately 30 times faster on the time axis and 20 times more in the change width than the Gibbs fixation and the tail suspension experiment of the experimental animal on the ground. This suggests that the elucidation of the mechanism of muscle atrophy using mice in the space is highly likely to be a seed for molecular target treatment for disuse muscle atrophy. In addition, muscle atrophy caused in the space is not limited to atrophy of morphological muscle fibers, but accompanies degenerative change of contraction function such as muscle weakness. This degenerative change, which is one of the aging phenomena indicators, is called Sarcopenia. But its onset mechanism is unclear in many cases, since there is no equivalent experimental system. It is speculated that the rapid muscle atrophy in the space is occurring in the combination of disuse atrophy and Sarcopenia. Therefore, we will comprehensively analyze gene expression and epigenomic change of skeletal muscle of mice bred at the International Space Station (ISS) using the next generation sequencer to identify candidate genes of muscle atrophy. After idetifing candidate genes, we will clarify how they are involved in muscle atrophy by analysis of skeletal muscle cell line and genetically modified mouse. It aims to clarify the muscle atrophy mechanism and to identify novel molecules that can be a target for disuse muscle atrophy and prevention and treatment against sarcopenia.