Development of a novel PDMS-based micro-nano device for evaluation of biological risk in Space – Publicly Invited Research 2018-2019
- A01 Ogura
- A01 H. Takahashi
- A01 S. Takahashi
- A01 Michiue
- A01 Hinoi
- A01 Tsumoto
- A01 Nikawa
- A01 Chatani
- A01 Kawakami
- A01 Akiyama
- A01 Tomita
- A03 Suzuki
- A03 Nakamura
- A03 Harada
- A03 Kobayashi
- A03 Miyamoto
- A03 Funayama
- A03 Kakinuma
| Research Subject | Development of a novel PDMS-based micro-nano device for evaluation of biological risk in Space |
|---|---|
| Research Group Leader |
 Professor, Collage of Science, Ibaraki University Website http://asakolab.sci.ibaraki.ac.jp/index.html (*Written in Japanese) |
| Research Collaborator(s) |
|
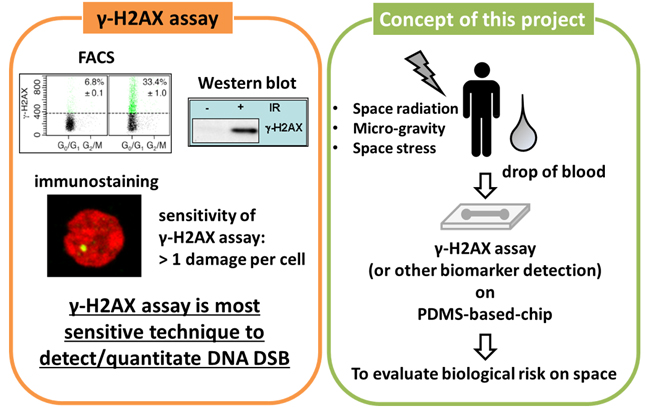
In modern society, exposure to radiation may come from cosmic rays, the sun or radioactive substances on the ground, during high altitude journeys, or in space. Therefore, exposure to ionizing radiation (IR) is one of the concerns to human health risk. Among the various DNA damages induced by IR, the DNA double-strand break (DSB) is the most dangerous damage leading to cancer. IR-induced DNA DSBs can be recognized using a sensitive quantitative assay based on the detection of phosphorylated H2AX (γ-H2AX) foci at the DNA break site, which can be visualized by both immunocyto- and immunohistochemistry techniques. Given its sensitivity (the γ-H2AX assay can detect responses to 1.2 mGy IR), γ-H2AX foci detection has been widely used for radiation biodosimetry. In this project, we aim to develop a novel micro-nano device which will allow us to monitor the DNA damage level by γ-H2AX assay on site, such as at a radiation accident site, in the International Space Station, and on Mars. We will proceed with a Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-based microfluidic system for the isolation of lymphocytes from whole blood cells and detection of γ-H2AX. In addition, we will identify novel radio-protective drugs for living in space.