Mechanisms of skeletal muscle homeostasis maintenance through crosstalk between the sensory nervous system and skeletal muscle satellite cells – Publicly Invited Research 2016-2017
- A02 Shinohara
- A02 Maekawa
- A02 Ohgami
- A02 Nishimura
- A02 Kawano
- A02 Iwase
- A02 Furuichi
- A02 Myung
- A02 Kitamura
| Research Subject | Mechanisms of skeletal muscle homeostasis maintenance through crosstalk between the sensory nervous system and skeletal muscle satellite cells |
|---|---|
| Research Group Leader |

|
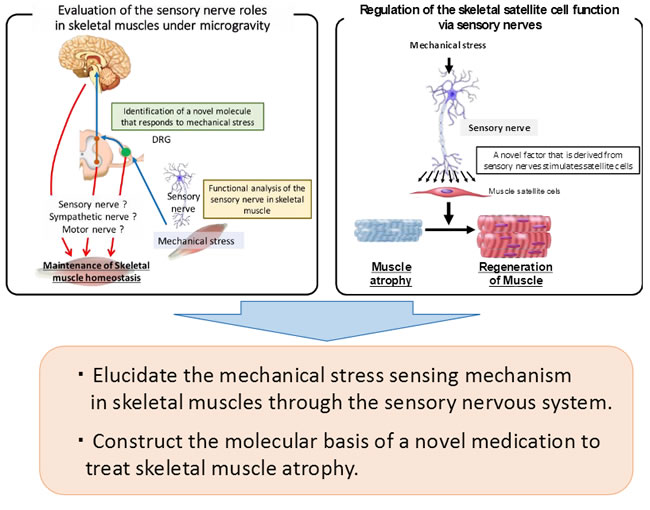
Elucidation of the mechanism of mechanical stress sensing is important for understanding skeletal muscle atrophy in microgravity environments. Our previous study reported that sensory nerves regulate bone metabolism under physiological conditions. Furthermore, sensory nerve dysfunction resulted in a significant decrease in bone regeneration in the bone marrow-ablated region. These observations suggest that the sensory nervous system may act as a mechanical stress sensing-organ, while also maintaining the function of tissue stem cells. Interestingly, muscle satellite cells are activated by mechanical/gravitational loads. In addition, muscle satellite cells respond quickly to mechanical stress and maintain their physiological function.
In this study, we focus on the interaction between the sensory nerves and muscle satellite cells and we clarify the mechanism of mechanical load sensing in skeletal muscles. These results will lead to the development of novel medications to treat muscle atrophy.
1. The mechanism of mechanical stress sensing in skeletal muscles through the function of sensory nerves.
1-1. Evaluation of the 3D anatomy of sensory nerves in skeletal muscle.
1-2. Analysis of the function of sensory nerves in skeletal muscles under microgravity.
2. The regulation of muscle satellite cells by the sensory nervous system.
2-1. Identification of a novel molecule in sensory nerves that responds to mechanical stress.
2-2. Analysis of the effects of a novel sensory nerve-derived molecule on muscle satellite cells.